标题:手机振动喇叭的金属弹片用什么材料比较好
18、20、2030、28是现在主流规格振动喇叭,在振动效果和可靠性、合格率之间的取舍是我头痛的问题,最近新设计一款18的,想做大功率,请教一下用什么材料的好一点?
想知道,请联系 QQ 79802351
18、20、2030、28是现在主流规格振动喇叭,在振动效果和可靠性、合格率之间的取舍是我头痛的问题,最近新设计一款18的,想做大功率,请教一下用什么材料的好一点?
介绍手机振动弹片的材料:
铍铜和钛铜,用做振动和接触弹片。
 此主题相关图片如下:弹片材料结构.jpg
此主题相关图片如下:弹片材料结构.jpg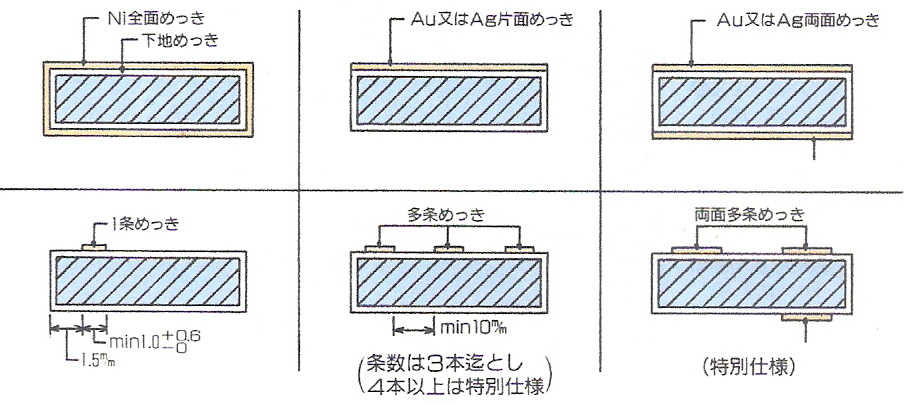
 此主题相关图片如下:弹片材质(铜及铜合金).jpg
此主题相关图片如下:弹片材质(铜及铜合金).jpg
中国 GB 1220-92 | 俄罗斯 GOST 5632-72 | 日本 JIS G4303-91 | 美国ASTM A276-96 | 比利时 BS970Part1 BSEN10088-1-95 | 德国 DIN17400-96 DINEN10088-1-95 | 法国 NFA35-578-91 NFEN10088-1-95 | ISO 683/13-86 TR4956/84 | |||
1Cr17Mn6Ni5N | - | SUS201 | 201 | X12CrMnNiN 17-7-5 | X12CrMnNiN 17-7-5 | X12CrMnNiN 17-7-5 | A-2 | |||
1Cr18Mn8Ni5N | 12KH17G9AH4 | SUS202 | 202 | X12CrMnNiN 18-9-5 | X12CrMnNiN 18-9-5 | X12CrMnNiN 18-9-5 | A-3 | |||
1Cr17Ni7 | - | SUS301 | 301 | BS970Part1-96 301S21 | - | NFA35-574-95 Z12CN17.07 | 14 | |||
1Cr18Ni9 | 12KH18H9 | SUS302 | 302 | 302S31 | DIN17440-96 X12CrNi18-9 | Z10CN18.09 | 12 | |||
Y1Cr18Ni9 | - | SUS303 | 303 | 303S31 | X12CrNiS18-9 | Z10CNF18.09 | 17 | |||
Y1Cr18Ni9Se | 12KH18H10E | SUS303Se | 303Se | 303S42 | - | - | 17a | |||
0Cr18Ni9 | 08KH18H10 | SUS304 | 304 | 304S31 | X5CrNi18-10 | Z7CN18.09 | 11 | |||
00Cr19Ni11 | 03KH18H11 | SUS304L | 304L | 304S11 | X2CrNi19-11 | X2CrNi19-11 | 10 | |||
0Cr19Ni9N | - | SUS304N1 | 304N | - | - | - | - | |||
0Cr19Ni10NbN | - | SUS304N2 | XM21 | - | - | - | - | |||
00Cr18Ni10N | - | SUS304LN | - | X2CrNiN18-10 | X2CrNiN18-10 | X2CrNiN18-10 | 10N | |||
1Cr18Ni12 | 12KH18H12T | SUS305 | 305 | X4CrNi18-12 | X4CrNi18-12 | X4CrNI18-12 | 13 | |||
0Cr23Ni13 | - | SUS309S | 309S | - | - | NFA35-578-91 Z15CN23-13 | 15 | |||
0Cr25Ni20 | - | SUS310S | 310S | 310S31 | - | Z8CN25-20 | 16 | |||
0Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 08KH17H13M2T | SUS316 | 316 | 316S31 | X5CrNiMo17-12-2 | Z7CND17-12-2 | 20 20a | |||
0Cr18Ni12Mo2Ti | 08KH17H13M2T | SUS316Ti | 316Ti S31635 | 320S31 | X6CrNiMoTi17-12-2 | X6CrNiMoTi17-12-2 | 21 | |||
00Cr17Ni14Mo2 | 03KH17H14M2 | SUS316L | 316L | 316S13 | X2CrNiMo18-14-3 | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 | 19 19a | |||
0Cr17Ni12Mo2N | - | SUS316N | 316N | X5CrNiMo17-12-2 | X5CrNiMo17-12-2 | X5CrNiMo17-12-2 | - | |||
00Cr17Ni13Mo2N | - | SUS316LN | 316LN | X2CrNiMo17-11-2 | X2CrNiMoN17-11-2 | X2CrNiMo17-11-2 | 19N 19aN | |||
0Cr18Ni12Mo2Cu2 | - | SUS316J1 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
00Cr18Ni14Mo2Cu2 | - | SUS316JIL | - | - | - | - | - | |||
0Cr19Ni13Mo3 | 08KH17H15M3T | SUS317 | 317 | 316S33 | X5CrNiMo17-13-3 | - | - | |||
00Cr19Ni13Mo3 | 03KH16H15M3 | SUS317L | 317L | Part-4 317S12 | X2CrNiMo18-15-4 | X2CrNiMo18-15-4 | 24 | |||
0Cr18Ni16Mo5 | - | SUS317J1 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
1Cr18Ni9Ti | 12KH18H10T | - | 321 | 321S31 | X6CrNitI18-10 | X6CrNiTi18-10 | 11 | |||
0Cr18Ni10Ti | 08KH18H10T | SUS321 | 321 | 321S31 | X6CrNiTi18-10 | X6CrNiTi18-10 | 15 | |||
0Cr18Ni11Nb | 08KH18H12B | SUS347 | 347 | 347S31 | X6CrNiNb18-10 | X6CrNiNb18-10 | 16 | |||
0Cr18Ni9Cu3 | SUSXM7 | XM7 | X3CrNiCu18-9-4 | X3CrNiCu18-9-4 | X3CrNiCu18-9-4 | - | ||||
0Cr18Ni13Si4 | - | SUSXM15J1 | XM15 | - | - | - | - | |||
0Cr26Ni5Mo2 | - | SUS329J1 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
1Cr18Ni11Si4AlTi | 15KH18H12G4TYU | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
0Cr13Al | - | SUS405 | 405 | 405S31 | X6CrAl13 | X6CrAl13 | 5 | |||
00Cr12 | - | SUS410L | - | - | - | Z3CT12 | - | |||
1Cr17 | 12KH17 | SUS430 | 430 | 430S17 | X6Cr17 | X6Cr17 | 8 | |||
YCr17 | SUS430F | - | - | X6CrMoS17 | - | 8a | ||||
1Cr17Mo | SUS434 | - | X6CrMo17-1 | X6CrMo17-1 | X6CrMo17-1 | 9c | ||||
00Cr30Mo2 | SUS447J1 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
00Cr27Mo | SUSXM27 | XM27 | - | - | - | - | ||||
1Cr12 | SUS403 | 403 | 410S21 | X6Cr13 | X6Cr13 | 3 | ||||
1Cr13 | 12KH13 | SUS410 | 410 | 410S21 | X12Cr13 | - | 3 | |||
0Cr13Ae | SUS405 | 405 | 403S17 | X6Cr13 | X6Cr13 | 1 | ||||
Y1Cr13 | SUS416 | - | 416S21 | - | X12CrS13 | 7 | ||||
1Cr13Mo | SUS410J1 | - | - | - | - | X12CrM126 | ||||
2Cr13 | 20KH13 | SUS420J1 | 420 | 420S37 | X20Cr13 | X20Cr13 | 4 | |||
3Cr13 | 30KH13 | SUS420J2 | 420 | 420S37 | X30Cr13 | X30Cr13 | 5 | |||
Y3Cr13 | SUS420F | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
4Cr13 | 40KH13 | - | - | X46Cr13 | X46Cr13 | X46Cr13 | - | |||
1Cr17Ni2 | 14KH17H2 | SUS431 | 431 | 431S29 | X17CrNi16-2 | X17CrNi16-2 | 96 | |||
7Cr17 | SUS440A | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
8Cr17 | SUS440B | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
9Cr17 | 95KH18 | SUS440C | - | - | - | - | - | |||
11Cr17 | SUS440C | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
Y11Cr17 | SUS440F | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
9Cr18Mo | SUS440C | 440C | - | - | - | - | ||||
9Cr18MoV | - | - | X90CrMoV18 | X90CrMoV18 | X90CrMoV18 | - | ||||
0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb | SUS630 | ASTM A564M-95 S17400 | - | - | ISO683/16-76 1 | |||||
0Cr17Ni7Al | 09KH17H7YU | SUS631 | 17700 | X7CrNiAL17-7 | X7CrNiAl17-7 | X7CrNiAl17-7 | 2 | |||
Grade 301 Temper ASTM A666 | Tensile Strength (MPa) min. | Yield Strength 0.2% Proof (MPa) min. | Elongation (% in 50mm) (thick.>0.76mm) min. | Bend Test (thickness > 1.27mm) | |
Bend Angle (°) | Factor | ||||
Annealed | 515 | 205 | 40 | - | - |
1/16 Hard | 620 | 310 | 40 | 180 | 1 |
1/8 Hard | 690 | 380 | 40 | 180 | 1 |
1/4 Hard | 860 | 515 | 25 | 90 | 2 |
1/2 Hard | 1035 | 760 | 18 | 90 | 2 |
3/4 Hard | 1205 | 930 | 12 | 90 | 3 |
Full Hard | 1275 | 965 | 9 | 90 | 5 |
Bend test is around a diameter of the Bend Factor multiplied by the steel thickness. | |||||
Physical Properties
Typical physical properties for grade 301 stainless steels are given in table B.
Table B. Physical properties of 301 grade stainless steel
| Grade | Density (kg/m3) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Mean Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (mm/m/°C) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m.K) | Specific Heat 0-100°C | Electrical Resistivity (nW.m) | |||
| 0-100°C | 0-315°C | 0-538°C | at 100°C | at 500°C | (J/kg.K) | ||||
| 301 | 8000 | 193 | 17 | 17.2 | 18.2 | 16.2 | 21.5 | 500 | 720 |
Possible Alternative Grades
304 The lower work hardening rate of 304 is acceptable, giving better ductility required for forming.
316 A higher corrosion resistance is required, and the lower work hardening rate of 316 can be compensated for.
Corrosion Resistance Corrosion resistance is similar to that of 304. Good resistance in applications involving external exposure to mildly corrosive conditions at ambient temperatures. Heat Resistance Good oxidation resistance in intermittent service to 840°C and in continuous service to 900°C, although not usually chosen for this environment. Heat Treatment Solution Treatment (Annealing) - Heat to 1010-1120°C and cool rapidly. Use low side of range for intermediate annealing. This grade cannot be hardened by thermal treatment. Cold Working Grade 301 and its low carbon variants are used where a high strength stainless steel is required. The grades work harden at the very high rate of approximately 14MPa/%Ra (14MPa increase in tensile strength for each 1% reduction of area of cold work), resulting in high achievable strengths from cold rolling and from roll forming. The strain-hardened austenite is at least partially transformed to martensite by this work. Despite the high strengths achieved there is still enough residual ductility to enable severe cold deformation. Although non-magnetic in the annealed condition, when cold worked the grade becomes strongly attracted to a magnet. Welding Good characteristics suited to all standard methods. Grade 308L filler rod is recommended. Welds in Grade 301 must be annealed for maximum corrosion resistance; this is not necessary in 301L or 301LN. Welding and post weld annealing will both remove high strength induced by prior cold rolling. Spot welding is commonly used to assemble cold rolled 301 components. The very small heat affected zone associated with this rapid welding technique results in little reduction of overall component strength. |
Applications Typical applications include: · Rail car structural components - often roll formed, brake pressed or stretch formed to profiles but also used flat. · Airframe sections · Highway trailer components · Automotive wheel covers · Wiper blade holders and clips · Toaster springs · Stove element clips · Screen frames · Curtain walls |
它是金属材料的重要性能指标之一。一般硬度越高,耐磨性越好。
常用的硬度指标有布氏硬度、洛氏硬度和维氏硬度。
HB布氏硬度,10mm球头、荷重3000kg,球头有三种类型:HBS标准球、HultGreen球、硬质合金球(碳化钨球HBW); 注意:一般称布氏硬度,默认是指HBW球头。
以一定的载荷(一般3000kg)把一定大小(直径一般为10mm)的淬硬钢球压入材料表面,保持一段时间,去载后,负荷与其压痕面积之比值,即为布氏硬度值(HB),单位为公斤力/平方mm (N/mm2)。
洛氏(ROCKWELL)
HRA/B/C,其中B标尺为球头,A、C标尺为金刚石锥形压头;事实上,HRA、HRB、HRC、HRD、HRE、HRF、HRG、HRH、HRK、HRL、HRM、HRP、HRR、HRS、HRV共15种标尺里面,只有HRC/HRA/HRD三个标尺的测量压头为金刚石,其他的全为球头。
当HB>450或者试样过小时,不能采用布氏硬度试验而改用洛氏硬度计量。它是用一个顶角120°的金刚石圆锥体或直径为1.59、3.18mm的钢球,在一定载荷下压入被测材料表面,由压痕的深度求出材料的硬度。根据试验材料硬度的不同,分三种不同的标度来表示:
HRA:是采用60kg载荷和钻石锥压入器求得的硬度,用于硬度极高的材料(如硬质合金等)。
HRB:是采用100kg载荷和直径1.58mm淬硬的钢球,求得的硬度,用于硬度较低的材料(如退火钢、铸铁等)。
HRC:是采用150kg载荷和钻石锥压入器求得的硬度,用于硬度很高的材料(如淬火钢等)。
*** 需要注意的是:洛氏硬度没有单位,它是以0.002毫米作为一个硬度单位。
维氏硬度(HV)
以120kg以内的载荷和顶角为136°的金刚石方形锥压入器压入材料表面,用材料压痕凹坑的表面积除以载荷值,即为维氏硬度值(HV)。 单位为公斤力/平方mm (N/mm2)。
实践证明,金属材料的各种硬度值之间,硬度值与强度值之间具有近似的相应关系。因为硬度值是由起始塑性变形抗力和继续塑性变形抗力决定的,材料的强度越高,塑性变形抗力越高,硬度值也就越高。

双磁是双面振动二合一的吗?现在就做了单面的,请问大家的音圈是找那几家供应商呢